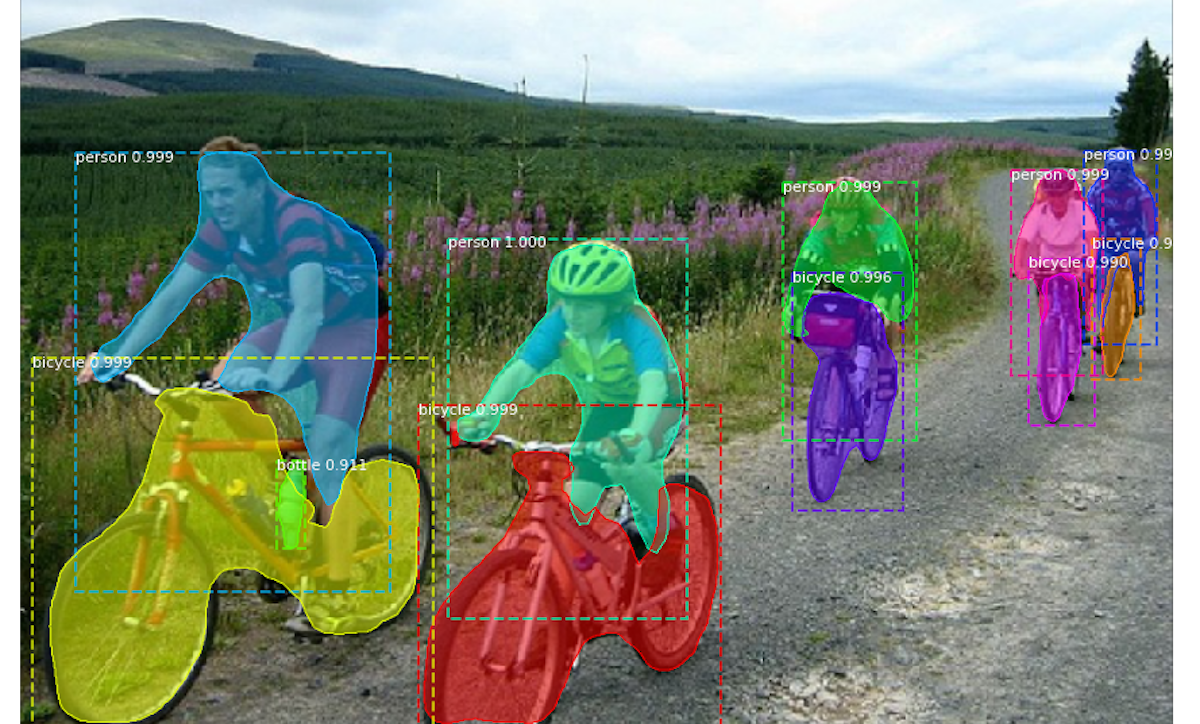
Mask R-CNN for Instance Segmentation- Summarized
In this post, we will discuss the use of region based object detector like Mask R-CNN to detect objects. Instead of creating a boundary box, image segmentation group pixels that belong to the same object.
Why Segmentation ?
-
Object detection basically gives only a bounding box, but does not give much of an information about the object.
-
Image segmentation creates a pixel-wise mask for each object in the image, which gives far more granular information of object(s) in the image.
-
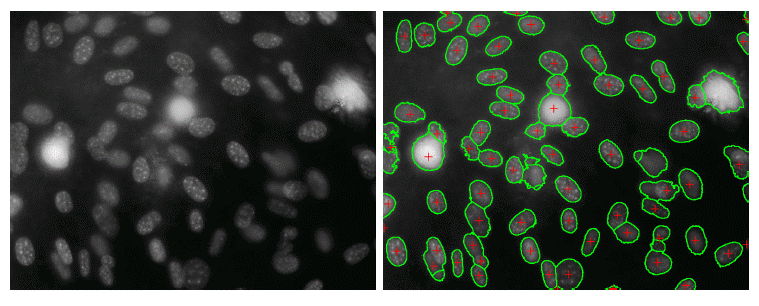
example: Cancerous cell detection
What is Image Segmentation ?
The process of dividing or partitioning the image into various parts called segments is known as Image Segmentation.
The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze.
Semantic Segmentation vs Instance Segmentation
Semantic Segmentation
- Classifies all the pixels of an image into meaningful classes of objects
- This is also known as dense prediction because it predicts the meaning of each pixel
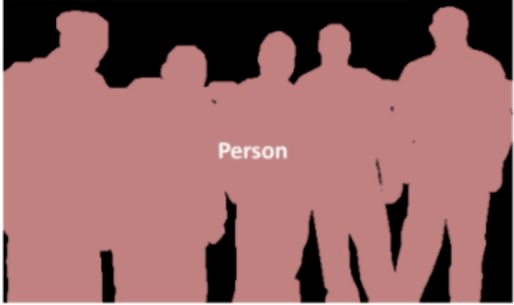
Instance Segmentation
- Identifies each instance of each object in an image.
Image Segmentation: Earlier methods
-
Thresholding:
- Divides an image into a foreground and background. A specific threshold value separates pixels into one of two levels to isolate objects. Thresholding converts grayscale images into binary images or distinguishes the lighter and darker pixels of a color image.
-
K-means Clustering:
- An algorithm identifies groups in the data, with the variable K representing the number of groups. The algorithm assigns each data point (or pixel) to one of the groups based on feature similarity. Rather than analyzing predefined groups, clustering works iteratively to organically form groups.
-
Histogram-based image segmentation:
- Uses a histogram to group pixels based on “gray levels”. Simple images consist of an object and a background. The background is usually one gray level and is the larger entity. Thus, a large peak represents the background gray level in the histogram. A smaller peak represents the object, which is another gray level.
-
Edge detection:
- Identifies sharp changes or discontinuites in brightness. Edge detection usually involves arranging points of discontinuity into curved line segments, or edges.
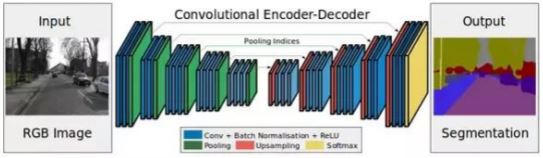
Image Segmentation: CNN based methods
- A general semantic segmentation architecture can be broadly thought of as encoder followed by a decoder network.
- Encoder: The encoder is pretrained classification network where the last fully connected layers are removed.
- Decoder: The task of the decoder is to semantically project the discriminative features (low resolution) learnt by the encoder onto the pixel space (higher resolution) to get the dense classification.
Deep Learning based Segmentation: Methods
-
Region Based Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- First the Bounding boxes are extracted, say segments of the image.
- Feed Segments of an image as input CNN which labels the pixels
- e.g. mask R-CNN
-
Fully Convolutional Networks
- Both encoder and decoder are convolutional layers.
- Can input any size inputs as it is fully convolutional
- e.g. U-Net architecture.
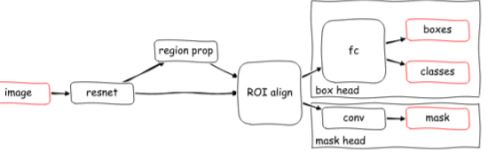
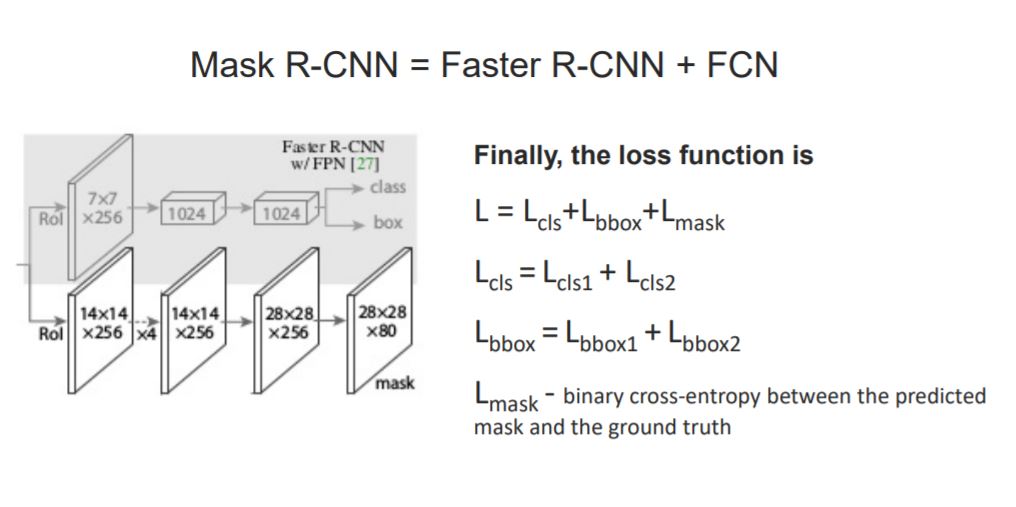
Mask R-CNN
Full paper: Mask R-CNN
-
Mask R-CNN is a state-of-the-art model for Instance segmentation. It extends Faster R-CNN, the model used for object detection, by adding a parllel branch for predicting segmentation masks.
-
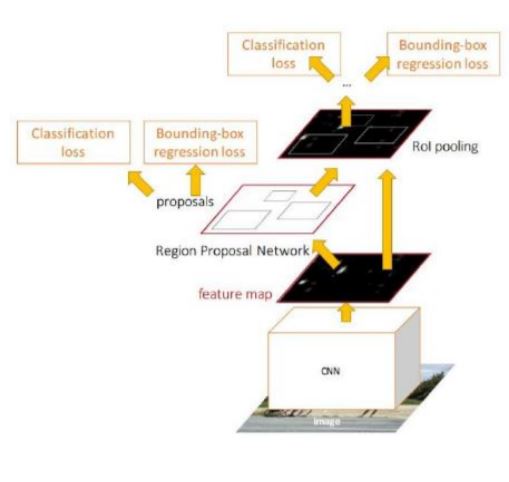
Faster R-CNN has two stages:
-
Deep convolutional network with Region Proposal Network (RPN) * Proposes regions of Interest (ROI) from the feature maps output by the convolutional neural network.
-
Fast R-CNN * Using RoI pooling layer, extracts feature maps from each RoI, and performs classification and bounding box regression.
Faster R-CNN
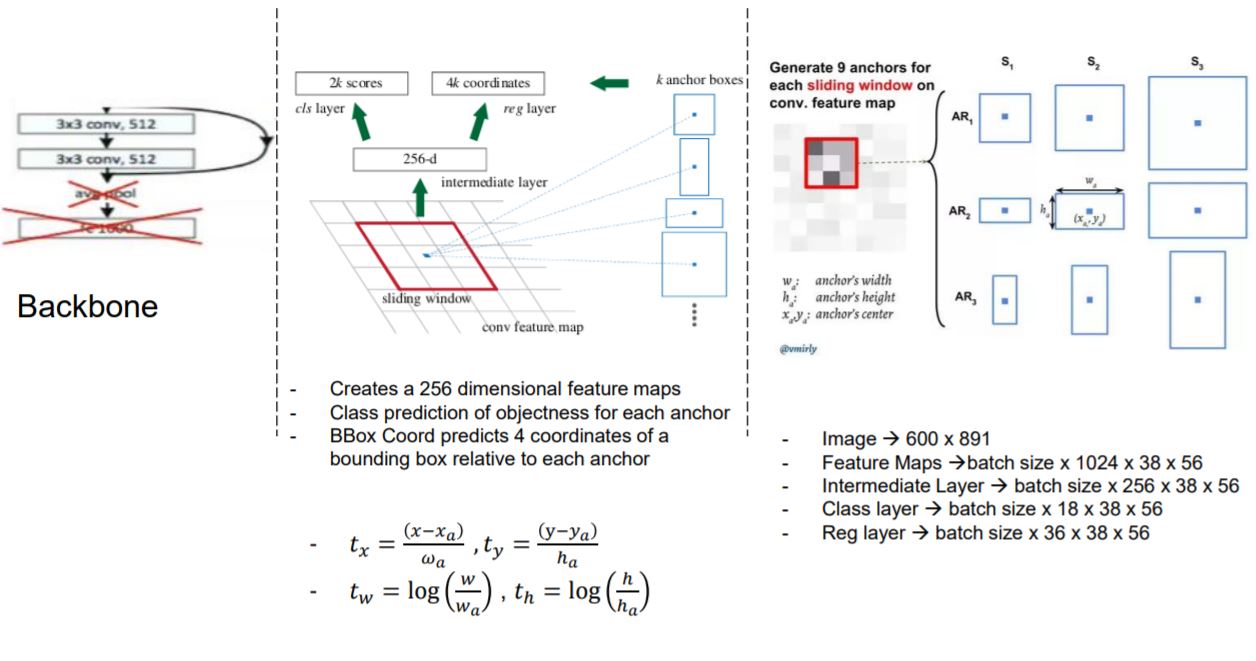
Stage 1: Deep convolutional network with RPN
-
So, if you have a feature map of 38 x 56 x 9 anchors, sampled at a stride of 16.
-
We would have (38569)/16 = 1192 proposals. That’s a lot of proposals !!!! for a single image.
-
RPN sorts the proposals to find the ones with the highest probability and cuts down on the low scoring proposals.
-
But we would still have a lot of proposals on the same object.
-
So, Non Maximal supression is applied to keep the most confident proposal and remove everything else that has an IOU > 0.7
Faster R-CNN
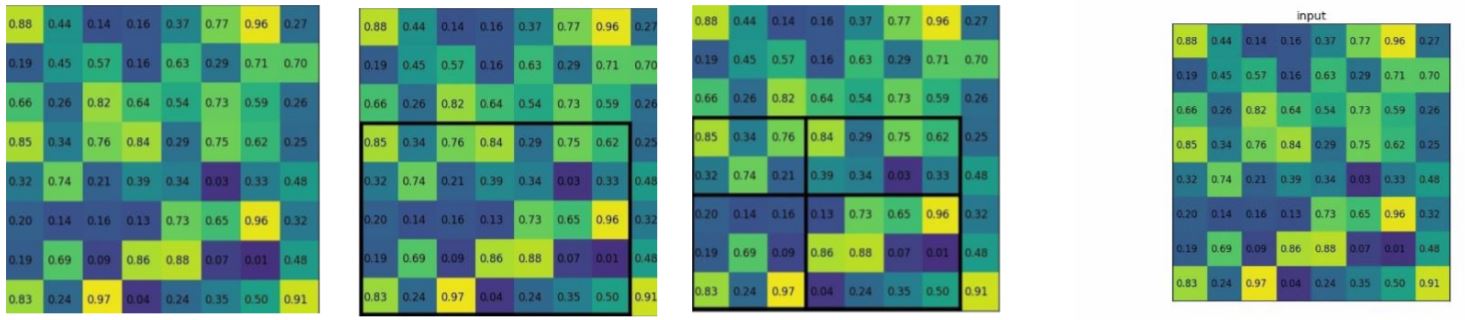
Stage-2: Fast R-CNN Using RoI Pooling Layer
- Three steps:
- Using RoI pooling layer, extracts feature maps from each RoI
The RoI pooling layer converts the section of feature map corresponding to each (variable sized) RoI into fixed size to be fed into a fully connected layer
-
Performs classification using fully connected layers
-
Bounding box regression (Same as in previous step).
Loss associated with Faster R-CNN
Training the Network
-
Train the RPN and final classifier and regressor separately.
-
Training RPN, final classifier and regressor toghether * 1.5 times faster.
Extension to predict mask- Mask R-CNN
-
References [1]:Mask R-CNN [2]:Mask R-CNN source code